AI Robo Explained: AI-powered robots are no longer confined to movies, research labs, or futuristic concepts. Today, intelligent robots clean homes, assist surgeons, deliver packages, manage warehouses, and even interact with humans using natural language. Yet, despite their growing presence, many people still wonder: How do AI robots actually work?
This article explains AI robots from the ground up—not with hype or jargon, but with clear, real-world explanations. Whether you’re a student, tech enthusiast, business owner, or curious reader, this guide will help you understand what makes robots intelligent, how they perceive the world, and how they decide what to do next.
What Is an AI Robot? (Simple but Accurate Definition)
An AI robot is a machine that can:
- Sense its environment
- Process information using artificial intelligence
- Make decisions autonomously
- Perform physical or digital actions
Unlike traditional robots that follow fixed instructions, AI robots can adapt, learn, and improve over time.
Key Difference:
- Traditional Robot → Follows pre-written rules
- AI Robot → Learns from data and experience
This ability to learn and adapt is what separates intelligent robots from simple automated machines.
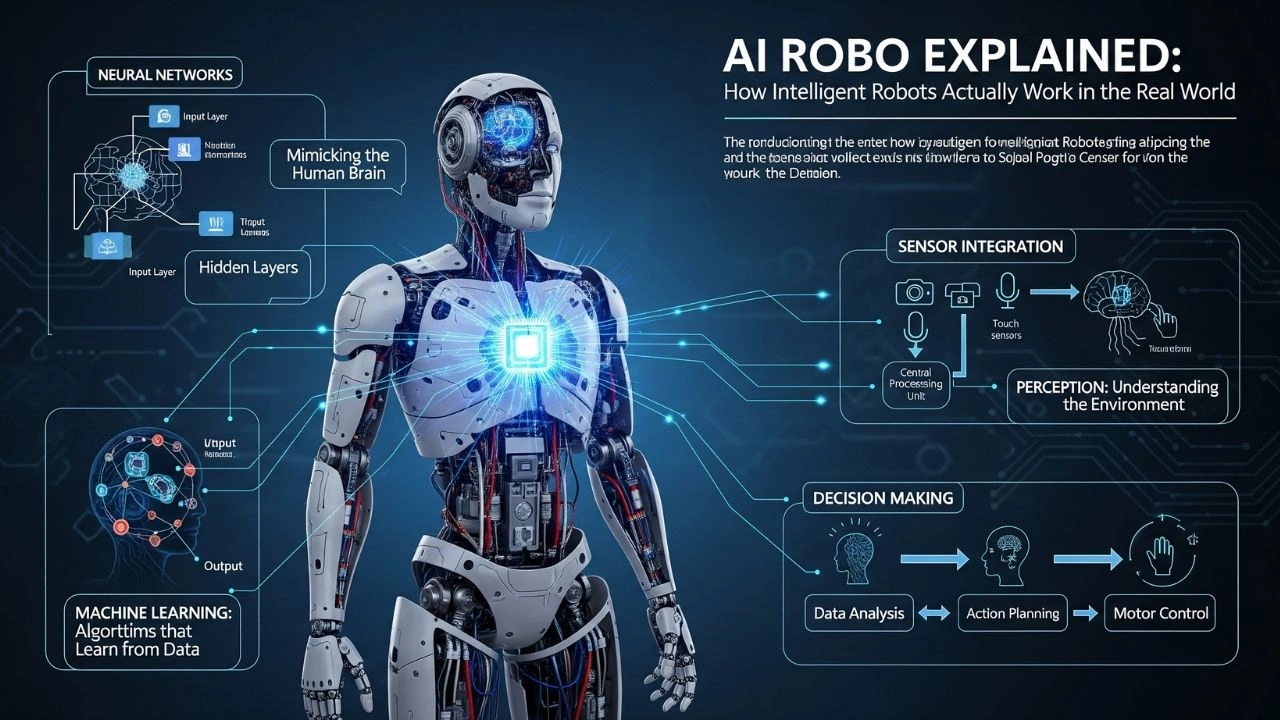
The Core Building Blocks of an Intelligent Robot
Every AI robot, regardless of its size or purpose, relies on five fundamental components:
- Sensors
- Processing Unit (Brain)
- Artificial Intelligence Software
- Actuators (Movement System)
- Feedback and Learning Loop
Let’s explore each in detail.
Read Also: Frase AI Review 2025: Is It the Smartest SEO Content Tool?
Sensors: How AI Robots “See,” “Hear,” and “Feel”
Sensors are the robot’s connection to the real world. Without sensors, a robot is effectively blind and deaf.
Common Robot Sensors Include:
- Cameras – vision and object recognition
- Microphones – sound and speech input
- Lidar & Radar – distance and depth measurement
- Touch Sensors – pressure and texture detection
- Temperature Sensors – heat and environment awareness
Sensors convert physical signals into digital data, which the robot’s AI can analyze and understand.
👉 Example:
A delivery robot uses cameras to identify obstacles and lidar sensors to measure distance, helping it navigate safely.
The Robot Brain: Processing Units and AI Models
Once sensor data is collected, it must be processed. This happens inside the robot’s “brain.”
What Acts as the Brain?
- CPUs (Central Processing Units)
- GPUs (Graphics Processing Units)
- AI Accelerators (TPUs, NPUs)
These processors run AI models trained to recognize patterns, predict outcomes, and make decisions.
Cloud vs Edge AI
- Edge AI: Processing happens inside the robot (faster, private)
- Cloud AI: Data is sent to servers (more powerful, scalable)
Modern AI robots often use a hybrid approach for speed and intelligence.
Artificial Intelligence Software: The Real Intelligence
The true intelligence of a robot comes from AI software, not hardware alone.
Core AI Technologies Used in Robots:
- Machine Learning
- Deep Learning
- Computer Vision
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Reinforcement Learning
These technologies allow robots to recognize objects, understand speech, plan actions, and improve performance over time.
How Machine Learning Enables Robots to Learn
Machine learning allows robots to learn patterns from data instead of relying on fixed programming.
How It Works:
- Robot receives data
- AI model analyzes patterns
- Errors are measured
- Model improves predictions
Over time, the robot becomes more accurate and efficient.
👉 Example:
A warehouse robot learns optimal routes by analyzing thousands of deliveries, reducing travel time automatically.
Reinforcement Learning: Teaching Robots Through Rewards
Reinforcement learning teaches robots using rewards and penalties.
Key Concepts:
- Action
- Environment
- Reward
- Policy
The robot tries different actions and learns which ones produce the best results.
👉 Used in:
- Self-driving cars
- Robotic arms
- Game-playing AI
This is how robots learn complex behaviors without being explicitly told what to do.
Computer Vision: How Robots Understand Images and Videos
Computer vision allows robots to interpret visual data.
Capabilities Include:
- Face recognition
- Object detection
- Gesture recognition
- Quality inspection
Using deep neural networks, robots can identify objects faster and more accurately than humans in some tasks.
👉 Example:
Factory robots inspect products for defects using computer vision, ensuring higher quality control.
Natural Language Processing: Talking to Robots Like Humans
Natural Language Processing (NLP) enables robots to understand and generate human language.
What NLP Allows:
- Voice commands
- Conversational responses
- Text understanding
- Multilingual support
AI robots combine NLP with speech recognition to interact naturally with humans.
👉 Example:
Service robots in hotels answer guest questions and provide directions using conversational AI.
Actuators: How Robots Move and Act
Actuators convert decisions into physical action.
Types of Actuators:
- Electric motors
- Hydraulic systems
- Pneumatic systems
They control:
- Wheels
- Arms
- Legs
- Grippers
The intelligence decides, but actuators execute.
Feedback Loops: How Robots Improve Over Time
AI robots operate in continuous feedback loops:
- Sense
- Decide
- Act
- Learn
This loop allows robots to:
- Detect mistakes
- Adjust strategies
- Improve efficiency
Feedback is essential for autonomy and safety.
Real-World Applications of AI Robots
AI robots are already transforming industries worldwide.
Healthcare
- Surgical robots
- Rehabilitation assistants
- Medication delivery
Manufacturing
- Assembly line automation
- Quality inspection
- Predictive maintenance
Logistics & Warehousing
- Autonomous forklifts
- Sorting robots
- Last-mile delivery
Home & Consumer Use
- Cleaning robots
- Smart assistants
- Elder care robots
Agriculture
- Crop monitoring
- Automated harvesting
- Precision spraying
Are AI Robots Dangerous? Understanding Safety and Control
A common concern is whether intelligent robots are dangerous.
The Reality:
- AI robots operate within defined limits
- Human oversight is mandatory
- Safety protocols are built-in
Safety Measures Include:
- Emergency stop systems
- Ethical AI guidelines
- Restricted decision boundaries
Robots do not have free will—they operate based on human-designed objectives.
Ethics and Trust: Responsible AI Robotics
Trust is critical for AI adoption.
Key Ethical Challenges:
- Bias in AI decision-making
- Data privacy
- Job displacement
- Transparency
Responsible robotics focuses on:
- Explainable AI
- Human-in-the-loop systems
- Fair and inclusive datasets
Ethical design ensures robots serve humanity, not replace it.
Read Also: Leading AI Companies in 2025-26: Who’s Winning the Global AI Race?
How AI Robots Will Evolve in the Future
The future of AI robotics includes:
- Emotion-aware robots
- Better human-robot collaboration
- Energy-efficient AI
- Self-learning multi-task robots
As AI models become more advanced, robots will become safer, smarter, and more helpful.
Who Should Learn About AI Robots Today?
Understanding AI robots is valuable for:
- Students and educators
- Entrepreneurs and business owners
- Engineers and developers
- Policy makers
- Everyday users
AI literacy is becoming a core life skill, just like computer literacy once was.
Conclusion: AI Robots Explained Clearly
AI robots are not magical beings or threats from science fiction. They are complex systems built from sensors, algorithms, and learning models, designed to solve real problems.
By understanding how intelligent robots actually work, we can:
- Use them more effectively
- Trust them responsibly
- Shape a better future with AI
The future is not humans vs robots—it’s humans with intelligent robots.